Artificial intelligence is evolving at breakneck speed, but building the infrastructure to power it requires a new type of facility: the AI factory. The term gained prominence when Nvidia pledged $100bn to build massive “AI factories” for OpenAI, redefining how we think about computing infrastructure. AI factories enable the deployment of advanced AI models and streamline large-scale AI operations.
In essence, an AI factory is a specialized computing environment designed to transform raw data into actionable insights. AI factories can also support the entire AI life cycle, from data ingestion to real-time data processing. Using AI factories allows organizations to scale AI initiatives effectively and manage the complexities of AI workloads.
These facilities are built to support sophisticated AI applications and ensure that AI models are trained efficiently. AI factories include essential components such as data pipelines, AI infrastructure, and robust data centers that optimize AI development processes.
As we look to the future, the benefits of an AI factory are clear: they allow for the efficient management of large amounts of data and enhance the capabilities of AI systems. AI factories streamline and optimize AI workflows, enabling organizations to leverage the full potential of AI and drive innovation across industries.
Key Takeaways — AI Factories & Infrastructure
AI Factory Meaning
An AI factory is a specialized data center designed to produce AI models and services at scale. Unlike traditional data centers that host websites, apps, or enterprise workloads, AI factories are designed for advanced AI inference tasks. Purpose-built for training and running large AI systems, AI factories are essential for advancing AI capabilities..
These facilities harness significant computational power and advanced infrastructure to facilitate the complex processes involved in developing artificial intelligence applications, from natural language processing to computer vision.

They are equipped with cutting-edge hardware, such as GPUs and TPUs, and employ sophisticated software frameworks that enable the efficient handling of vast amounts of data necessary for training AI models.
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang has described them as critical for the future of AI inference. “gigantic factory investments”, where the product is not physical goods, but intelligence.
This concept emphasizes the shift in focus from traditional manufacturing to the creation of advanced algorithms and machine learning systems that can learn and adapt over time, ultimately transforming industries and enhancing productivity across various sectors.
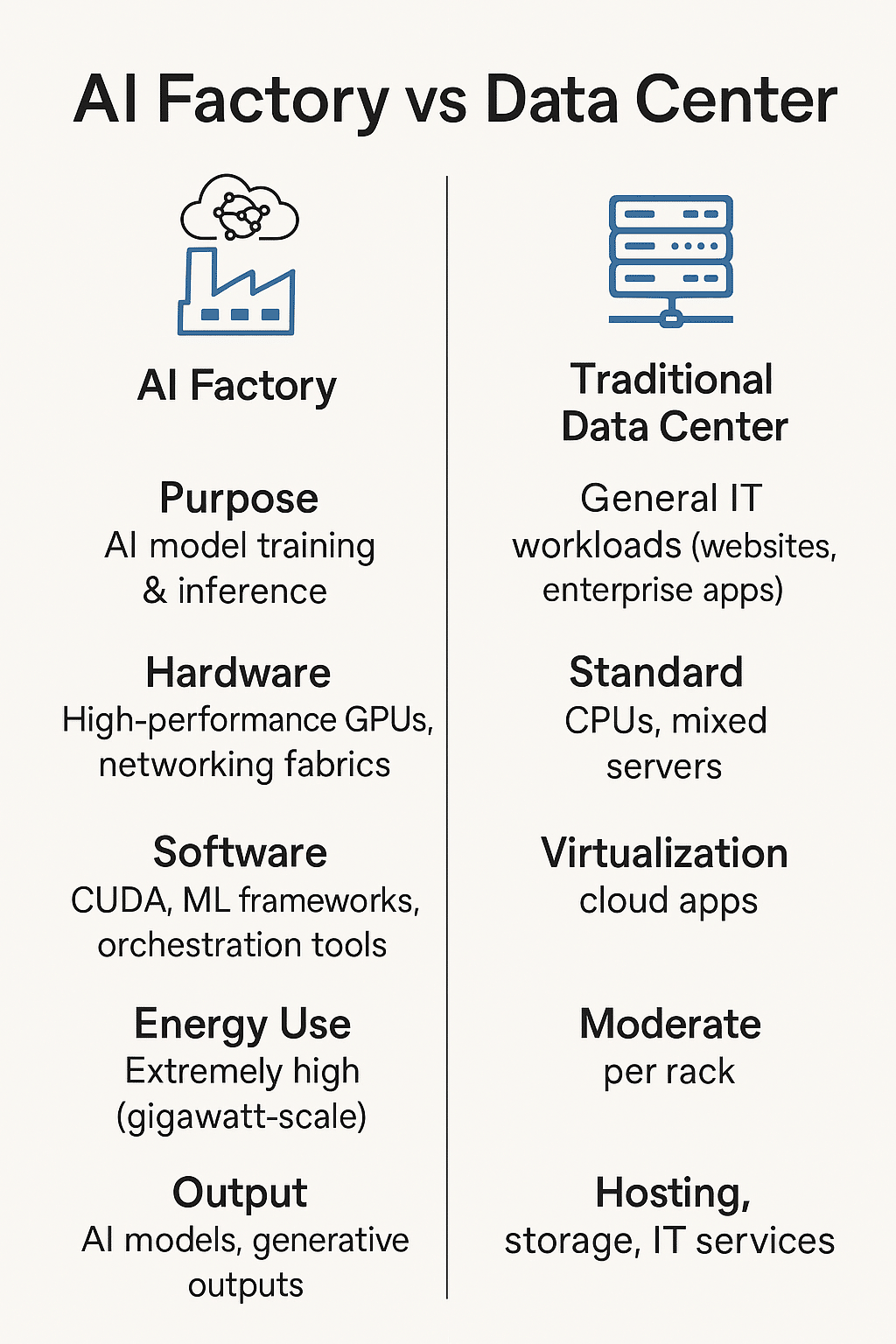
AI Factory vs Data Center
Although AI factories share similarities with data centers, they are not the same.
| Feature | Traditional Data Center | AI Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | General IT workloads (websites, enterprise apps) | AI model training & inference |
| Hardware | Standard CPUs, mixed servers | High-performance GPUs, networking fabrics |
| Software | Virtualization, cloud apps | CUDA, ML frameworks, orchestration tools |
| Energy Use | Moderate per rack | Extremely high (gigawatt-scale) |
| Output | Hosting, storage, IT services | AI models, generative outputs |
In short, the advancements in AI adoption are transforming industries. AI factories are the next evolution of data centers, optimized entirely for AI compute.
How an AI Factory Works
AI factories bring together:
- Compute: Specialized GPUs (e.g., Nvidia H100, B200) optimized for parallel workloads.
- Networking: High-bandwidth interconnects for distributed training.
- Storage: Petabytes of fast-access memory for handling massive training datasets.
- Software Stack: CUDA, PyTorch, TensorFlow, and orchestration platforms to manage workloads.
These systems train large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and serve billions of inference requests weekly.
Costs & Scale of Generative AI Factories
Building an AI factory is astronomically expensive. Nvidia estimates that every AI factory’s data requirement is significant for optimal performance. 1 gigawatt (GW) of AI infrastructure requires $50 billion in hardware.
- Nvidia’s latest deal with OpenAI calls for at least 10GW of compute, implying costs of $500–600bn is the estimated investment needed for AI factories to meet growing demand for AI solutions..
- Morgan Stanley projects Nvidia could capture $350bn of that in hardware sales.
This is why some analysts call AI factories the “arms race of the decade.”
Components of an AI Factory
An AI factory is a specialized computing environment designed to streamline and optimize the AI development process, ensuring that AI models are effectively trained and deployed. The core components of an AI factory include advanced AI infrastructure and sophisticated data pipelines that facilitate the ingestion, processing, and transformation of raw data into actionable insights.
AI factories enable the management of large-scale AI workloads, allowing organizations to scale AI initiatives and deploy AI applications more efficiently. By employing real-time data processing and AI reasoning capabilities, these factories ensure that AI outputs meet the demands of modern AI operations.

Additionally, AI factories are built to support the entire AI lifecycle, from data ingestion to AI inference, thereby maximizing the value derived from data and enhancing the benefits of AI adoption in various industries. Overall, AI factories are essential for implementing advanced AI solutions that leverage the power of generative AI and advanced robotics in the age of AI.
Energy & Environmental Impact of Building AI Factories
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that 10GW of AI factories consume as much electricity annually as 10 million US households, highlighting the energy demands of AI capabilities.
This creates challenges:
- Securing stable power supply at scale.
- Transitioning to renewable sources to reduce carbon impact.
- Managing cooling and efficiency.
Without innovation, AI factories risk becoming one of the world’s largest industrial consumers of energy.
Current AI Factory Projects
- Nvidia + OpenAI ($100bn deal): Massive investment to build AI factories powering ChatGPT.
- OpenAI Stargate Project: A $400bn collaboration with Oracle and SoftBank to deploy 5 US-based data centers.
- Competitors: Google, Meta, Anthropic, and Elon Musk’s xAI are all racing to build comparable AI infrastructure.
- China: Alibaba and DeepSeek are investing heavily in GPU-based AI factories.
Strategic Implications
- Nvidia’s Dominance: Its CUDA platform locks developers into Nvidia GPUs, similar to Microsoft Windows in the PC era.
- Supply Chain Reliance: From Foxconn to Broadcom, the AI factory supply chain is stretched thin, impacting the availability of components of an AI factory.
- Economic Risk: Bain projects the industry may miss revenue targets by $800bn by 2030, raising sustainability concerns.
Benefits of an AI Factory
An AI factory refers to a systematic approach to developing and deploying artificial intelligence technologies at scale. One of the primary benefits of an AI factory is its ability to streamline the process of AI model development, allowing organizations to quickly translate new data into actionable insights.
This efficiency not only reduces the time required to bring new AI solutions to market but also enhances collaboration among data scientists, engineers, and business stakeholders. Additionally, an AI factory promotes the standardization of best practices in AI development, ensuring that models are built with scalability and reliability in mind.

By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, organizations can leverage an AI factory to drive better decision-making, optimize operations, and ultimately gain a competitive edge in their industry.
AI factories are transforming industries by enabling advanced robotics and managing the entire AI lifecycle through high-performance computing and real-time data. The value from data can be maximized by managing the entire data process effectively, leading to the successful deployment and operation of sophisticated AI models.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the meaning of AI factory?
An AI factory is a specialized data center that produces AI models and services at scale, powered by GPUs, high-bandwidth networking, and massive energy inputs.
2. How is an AI factory different from a traditional data center?
AI factories focus solely on AI training and inference, while data centers handle broader IT workloads.
3. How much does an AI factory cost to build, considering the necessary components of an AI factory?
Around $50bn per gigawatt, with mega-projects costing hundreds of billions.
4. How much energy does an AI factory use?
10GW of AI compute power equals the annual electricity use of 10 million US homes.
5. Who is building AI factories?
Nvidia (with OpenAI), OpenAI’s Stargate (with Oracle, SoftBank), Google, Meta, Anthropic, xAI, and Chinese players like Alibaba are all key players in the AI solutions landscape.
Conclusion
AI factories represent the future of computing with their specialized focus on AI capabilities. next frontier of computing infrastructure. They are reshaping the balance of power in AI, with Nvidia positioning itself as the indispensable supplier of hardware and software.
The question is not whether AI factories will exist — but who controls them, and how the world will manage their costs, energy needs, and global impact.

